UV light glue for industry
- Controlled UV light curing
- Transparent final assembly
- High mechanical strength
- Very fast bonding
Quote
Close
You request has been sent.
We promise to respond to you in detail within 24 hours.
In the meantime, feel free to browse our other products.
What is UV glue - or light-curing adhesive?
Main characteristics:

- Single-component, solvent-free adhesive containing photoinitiators
- Liquid adhesive, with variable viscosity depending on the type
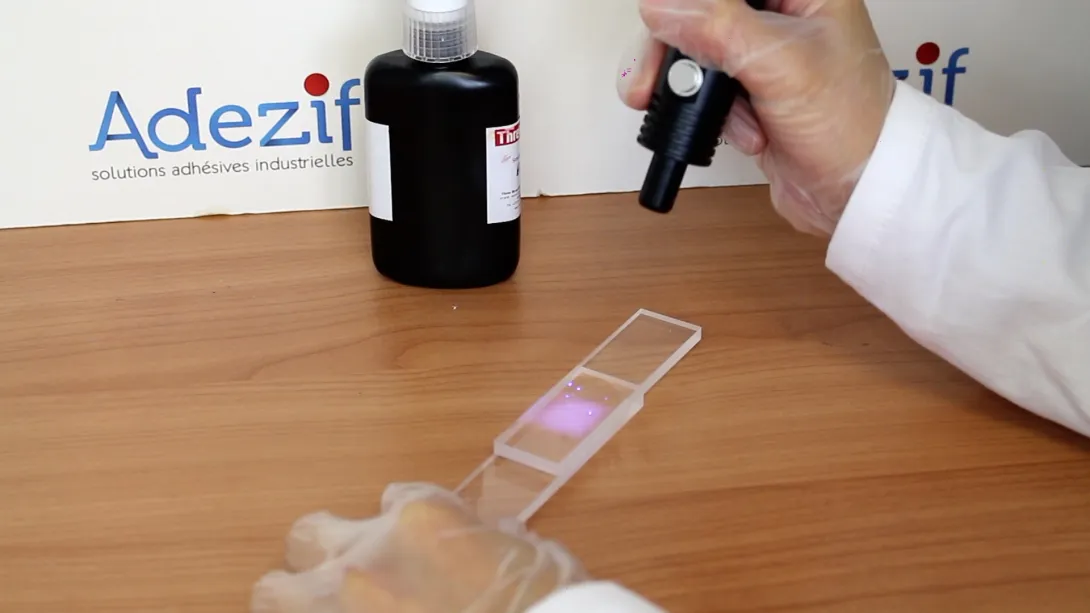
- Cures only when exposed to UV light with appropriate wavelength
- Almost instantaneous adhesion under UV light
- Optically transparent: discreet and aesthetic final assembly
Compatible materials:
UV activated glues are frequently used for bonding glass or hard plastics (PMMA, PVC, etc.) to similar substrates or to other materials (metal, leather, wood, rubber, ceramics, etc.).
In general, UV adhesives work well with the following glasses: clear float, mirrors, tempered glass and wired mirror glass.
They can be more difficult to use on structured glass, like shaped glass.
In all cases, one of the substrates to be bonded must be transparent to UV radiation which activate the curing of the adhesive.
UV glues can be used on machined surfaces that have lost their transparency. They become translucent again on contact with the adhesive.
Important: Choose a UV light glue that is adapted to the nature of your surfaces!
4 main types of UV adhesives:
- Acrylic UV adhesives
- Cyanoacrylate UV adhesives
- Silicone UV adhesives
- Epoxy UV adhesives
Glues that cures with UV light generally have very good mechanical resistance. Some of them even perform similarly or better than conventional epoxy adhesives.
Curing time of UV glue
Complete polymerization usually takes places after 10 to 30 seconds of UV exposure.
However, polymerization time depends on several factors:
- Spectrum of the UV lamp: photoinitiators included in UV glues are variable and activate the polymerization chen the UV spectrum of the lamp matches them (365 nm or 405 nm).
An inadequate UV wavelength can slow or block the polymerization. - Distance between the lamp and the adhesive: position the lamp as close as possible.
- Glue thickness: this is specified in the data sheets.
- Materials used: for instance, some plastics absorb UV light and slow down the curing process.
How to use and apply a UV adhesive ?
- Clean the surfaces to be assembled: see our page on surface preparation and cleaning for adhesive bonding.
- Apply the UV activated glue avoiding the formation of bubbles.
- Position the surfaces, avoiding any tension in the assembly.
- Wipe off excess glue with a lint-free cloth.
- Expose to UV light to initiate the polymerization.
Precautions for use:
Ultraviolet light bonding requires proper protective equipment:
- UV protective goggles
- Suitable gloves
- A suit and/or UV protection sheets in case of intensive emission
Keep the UV glue in its original, well closed bottle, away from natural and artificial light.
Use is not recommended in the presence of pure oxygen and chlorine.
How to choose the right UV adhesive ?

- Choose a UV light glue according to the requirements of the materials to be bonded, the strength needed and the final use of the assembly.
- Check technical data to ensure that the UV spectrum of the lamp corresponds to the chosen UV glue.
- Areas not accessible to UV light: choose a multi-purpose adhesive such as Loctite 3526 UV glue which has the ability to cure at 120°C for 15 minutes.
- Areas that are difficult to access: use an ultra fluid UV glue that will spread by capillary action.
Contact our experts to find the ideal UV adhesive for your application!
Industrial applications of UV bonding
Thanks to its instantaneous polymerization, UV adhesive is perfectly suited to fast production cycles.
Advantages:
- You can follow the different production steps without waiting for the adhesive to dry
- Quality control can be easily integrated by using a UV lamp
UV glues are often used for applications in POS/POP, automotive, electronics, medical, telecommunication, furniture industry or decoration.
Some examples of applications:
- Gluing ornaments to glass
- Fixing metal handles to glass doors
- Gluing metal frames to glass panels
- Museum display cases
- Mounting displays or other POS accessories
Some of our references
Immediate polymerization under UV light. High temperature resistance (150°C). Assembly, sealing, coating...

Fast fixturing, fillet or surface cure. For plastics, metals and rubbers. Qualified to ISO 10993 protocol: use in disposable medical devices.

UV curing adhesive ideal for plastic and glass. Forms a solid and transparent glue joint. Heat curing possible.

High resistance to humidity and chemicals. UV curing. Adheres on a wide variety of substrates.

Durability and chemical resistance. UV and visible light curing. Strong adhesion.

Dual polymerization: contact and UV. Fast setting on multiple substrates, fills gaps. Low odor, low blooming.